KetosisA Deep Dive into the Metabolic State Transforming Health and Wellness Imagine your body as a hybrid car, capable of running on two distinct fuel sources: gasoline (carbohydrates) and electricity (fat). Ketosis is like switching your body’s engine from gasoline to electricity, primarily using fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates…. Read More is like switching your car from gasoline to electricity. Normally, our bodies primarily use carbohydratesCarbohydrates, often called carbs for short, are organic molecules that your body uses for energy. They’re one type of fuel the body can use for energy. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, hence the name “carbohydrate” (carbo = carbon, hydrate = water). They come in simple… Read More (sugarsSugar is a substance represented as a simple carbohydrate (a basic type of molecule made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) that serves as a vital component throughout the body. It is the primary source of energy for most cells, acting like the body’s main fuel. Every part of the body,… Read More and starchesImagine tiny packets of sugar stashed away in a plant. Starch is exactly that! It’s a complex carbohydrate molecule that plants use to store energy for later use. It’s like nature’s built-in pantry, providing a slow and steady source of energy when needed. While not directly involved in human metabolism… Read More) for fuel. However, when carbs are scarce, our bodies shift into ketosis. This metabolicMetabolism is the set of chemical processes that happen inside the body to keep it alive and working. Think of the body as a busy kitchen where food is turned into energy, building blocks, and waste. These processes break down food to release energy, build new cells, and remove unwanted… Read More state involves converting stored fat into moleculesImagine tiny building blocks that come together to form everything around you, from water to air to your own body! A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by strong forces called chemical bonds. Think of them as the microscopic Legos that build the world! The… Read More known as ketonesKetones, organic compounds produced by the liver, are the unsung heroes of energy metabolism, stepping in when glucose, the body’s primary fuel, becomes scarce. Think of them as a reserve power generator, kicking into gear when the main power supply (carbohydrates) is low. While often associated with the ketogenic diet,… Read More, which our organsIn the context of the body, an organ is a distinct part made up of different tissues (groups of similar cells working together) that are organized to perform one or more specific functions. Familiar examples of organs include the heart, which pumps blood; the lungs, which facilitate breathing; and the… Read More and tissues can then use for energy.
Detailed EtymologyEtymology is the study of the origin and history of words. It’s like detective work, tracing how words have changed over time and moved between languages. Think of it like this: • Words have a long history, just like old family stories. • Etymology digs into those stories to see… Read More
The term “ketosis” derives from the word “ketone,” a type of organicThe word “organic” has two main meanings related to living organisms and the natural world. Here’s a breakdown of its definition, origin, and how it applies to food and health: Etymology and Origin: • Origin: The word “organic” stems from the ancient Greek word “organon” (ὄργανον) meaning “instrument, tool, or… Read More compound. “Osis” is a suffix often used in medical terminology to denote a condition or process. Thus, “ketosis” describes the state of having elevated ketone levels in the body. The concept of ketosis gained prominence in the early 20th centuryA century is a period of 100 years. Examples: • The 21st Century: The years 2000 to 2099. • The 19th Century: The years 1800 to 1899. • The 8th Century BC: The years 800 BC to 701 BC. Etymology: The word “century” comes from the Latin word “centuria,” which… Read More with the development of the ketogenic diet1. Simple Definition: Imagine your body is like a hybrid car with two fuel tanks: one for gasoline (sugar) and one for electricity (ketones). The ketogenic diet, or keto diet, is like switching your car’s engine to run primarily on electricity. This means you drastically reduce your intake of carbohydrates… Read More, originally used to treat epilepsy in children.
Real-World Applications
- Medical Conversations: “Your bloodBlood is the life force coursing through your veins and arteries, delivering vital oxygen and nutrients to every cell in your body while whisking away waste products. It’s a complex, dynamic fluid—not just a simple red liquid. Consider it a bustling highway system within your body, carrying various cellular vehicles… Read More tests show elevated ketone levels, indicating that you are in ketosis.”
- Lab Reports: “UrinalysisUrinalysis (UA), a simple yet powerful diagnostic tool, offers a window into the body’s internal workings. It is a thorough examination of urine, the liquid waste product that the kidneys filter. By analyzing the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine, the UA can reveal valuable clues about kidney function,… Read More positive for ketones, consistent with ketosis.”
- Dietary Discussions: “I’m following a ketogenic diet to promote ketosis and weight loss.”
Contextual Information: The Ketosis Cascade
Ketosis is a natural metabolic process that occurs when the body shifts from using carbohydrates to fatsThe substance known as fat occupies a role far more complex and vital than often perceived. While frequently discussed in terms of diet and appearance, this tissue, properly termed adipose tissue when referring to the cellular mass, is a dynamic and essential component supporting a myriad of the body’s critical… Read More as its primary energy source. A significant reduction in carbohydrate intake, frequently combined with an increase in fat consumption, causes this shift.
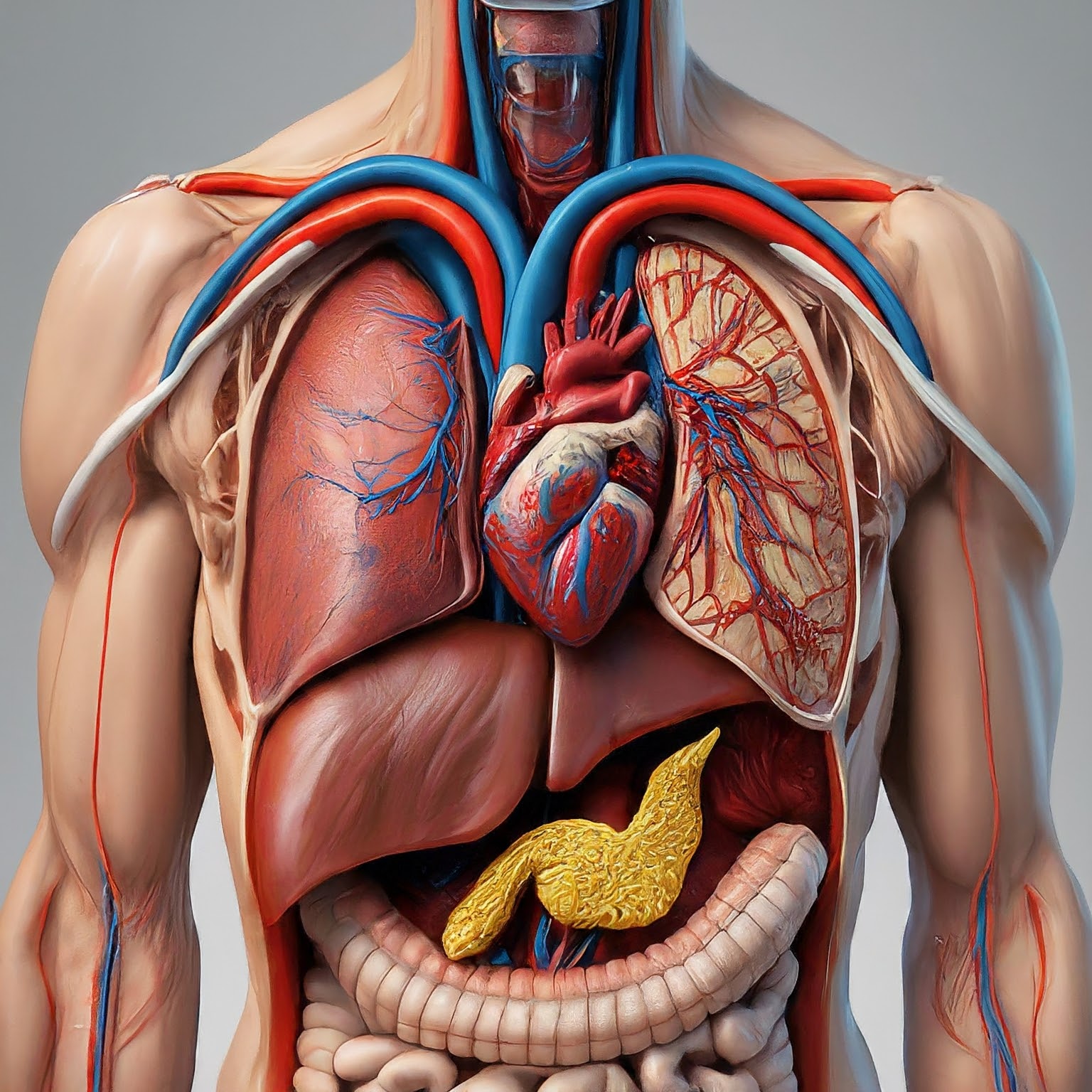
Here’s how the major organs involved in ketosis play their roles:
- LiverThe liver is a large organ located in the upper right part of the belly, under the rib cage. Like the heart that pumps blood or the lungs that help with breathing, the liver plays a crucial role in keeping the body healthy and working properly. This important organ is… Read More: The liver is the star player in ketosis. When carbs are scarce, it begins converting fatty acids into ketones. The primary ketones produced are acetoacetateAcetoacetate is another type of ketone body produced by your liver during ketosis, alongside Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB). It’s like a partner in the ketone fuel production team. Explanation: Think of it like this: • When your body is low on carbs and needs to burn fat for energy, it creates ketones…. Read More, beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)BHB is one of three main ketone bodies produced during a metabolic state called ketosis. Ketosis occurs when your body shifts from primarily burning carbohydrates for energy to burning fat. This shift can happen naturally through fasting or when following a low-carb, high-fat diet like the ketogenic diet. BHB is… Read More, and acetone1. Simple Definition: Acetone is a chemical that your body can make, kind of like a factory producing a product. It’s a simple, colorless liquid that has a strong, sweet smell. Think of it as a kind of fuel your body can use when it’s low on its preferred energy… Read More. These ketones are then released into the bloodstream to be used as fuel by other organs.
- PancreasThe pancreas, a vital organ nestled behind the stomach in the abdomen, serves as a critical crossroads for bodily function, playing a significant role in both digestion and metabolism. While often less discussed than the heart or brain, its proper operation is indispensable for the health of the entire body,… Read More: The pancreas produces insulinYour pancreas produces the super hormone insulin, which is essential to your body’s metabolism. Here’s a breakdown to make it clear: Definition: Insulin acts like a master key that unlocks the door for sugar (glucose) to enter your cells. Glucose is the main source of energy for your body, and… Read More, a hormoneImagine your body is a giant kingdom with many different jobs to be done. Hormones are like the royal messengers, carrying messages from one part of the body to another to keep everything running smoothly. • Other Names: You might not hear other names for hormones very often, but sometimes scientists… Read More that regulates blood sugarBlood sugar, also known as blood glucose, is a type of simple sugar circulating in your bloodstream. It can be a primary source of energy for your cells. Your body can get blood sugar from carbohydrates that you eat. The Word “Blood Sugar” This term is a modern invention, emerging… Read More levels. In ketosis, insulin levels decrease, signaling the body to switch to fat burning. This reduced insulin response also helps to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Kidneys: The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste products from the blood, including excess ketones. During ketosis, the kidneys excrete some ketones in the urine, which can be measured using urine test strips. The kidneys also help to maintain electrolyte balance, which can be challenged in ketosis due to increased urination.
- Heart: The heart readily adapts to using ketones as an energy source. Some studies even suggest that ketones may improve heart function and protect against cardiovascular disease. However, more research is needed to confirm these potential benefits.
Research Insights: The Sugar-Ketosis Seesaw
Sugar intake directly influences ketosis. High sugar consumption provides the body with ample glucoseGlucose, a simple sugar (a sweet substance the body uses for energy), serves as a vital component in the human body, acting as the primary fuel for cells (tiny units that make up the body). Imagine the body as a bustling factory, where glucose is like the electricity powering the… Read More (a type of sugar), inhibiting ketone production. To enter ketosis, carbohydrate intake must be significantly reduced, forcing the body to turn to fat stores for energy.
- A 2013 study published in the “European Journal of Clinical Nutrition” demonstrated that a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet effectively induced ketosis in adults with obesityObesity is a medical condition where someone has excessive body fat that can negatively affect their health. It’s not just about weight, but also about the amount of fat that accumulates in the body, especially around the belly. Etymology: The word “obesity” has a long history, dating back to the… Read More.
- A 2018 review article in “Current Developments in Nutrition” discussed the potential therapeutic applications of ketosis for various conditions, including epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancerImagine your body as a well-organized society, where each cell plays a specific role. Cancer disrupts this harmony, as a group of cells goes rogue, breaking the rules of normal growth and function. These renegade cells multiply uncontrollably, forming tumors that invade and damage surrounding tissues. Origins of the Word… Read More.
Additional Facets
- Ketoacidosis1. Simple Definition: Imagine your body as a car with two fuel tanks: one for gasoline (sugar/glucose) and one for a special kind of fuel called ketones. Ketoacidosis happens when your body runs out of gasoline and starts using way too much of the ketone fuel. This overload of ketones… Read More vs. Ketosis: It’s important to distinguish between ketosis and ketoacidosis. Ketosis is a natural metabolic state, while ketoacidosis is a dangerous complication of diabetesDiabetes is a chronic condition where your body struggles to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. Glucose is like fuel for your cells, and it comes from the food you eat. Insulin, a hormone made by your pancreas, acts like a key that unlocks cells, letting glucose in to provide energy…. Read More characterized by extremely high ketone levels and can be life-threatening.
- “Keto Flu”: Some people experience flu-like symptoms when first starting a ketogenic diet, often referred to as the “keto flu.” This is usually mild and temporary, and can be mitigated by staying hydrated and replenishing electrolytesImagine your body as a vast network of interconnected wires, each carrying electrical impulses essential for life. Electrolytes are the tiny charged particles that create this vital current. They’re not some futuristic technology; they’re minerals dissolved in your body fluids, like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. These tiny powerhouses help… Read More.
- Foods for Ketosis: High-fat foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish are staples of a ketogenic diet. Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and spinach are also important for providing fiberImagine your digestive system as a river, carrying essential nutrients to every corner of your body. Fiber acts like a gentle current, helping to move things along smoothly and efficiently. It’s the indigestible part of plant foods that your body can’t break down, but it plays a crucial role in… Read More and nutrients.
Summary and Conclusion
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the body switches from using carbohydrates to fats as its primary fuel source. The liver produces ketones in this shift, which the heart and brain then use as a source of energy. The pancreas, kidneys, and heart all play essential roles in adapting to and maintaining ketosis. While ketosis can have potential health benefits, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on a ketogenic diet to ensure it’s appropriate for your individual needs and health status.