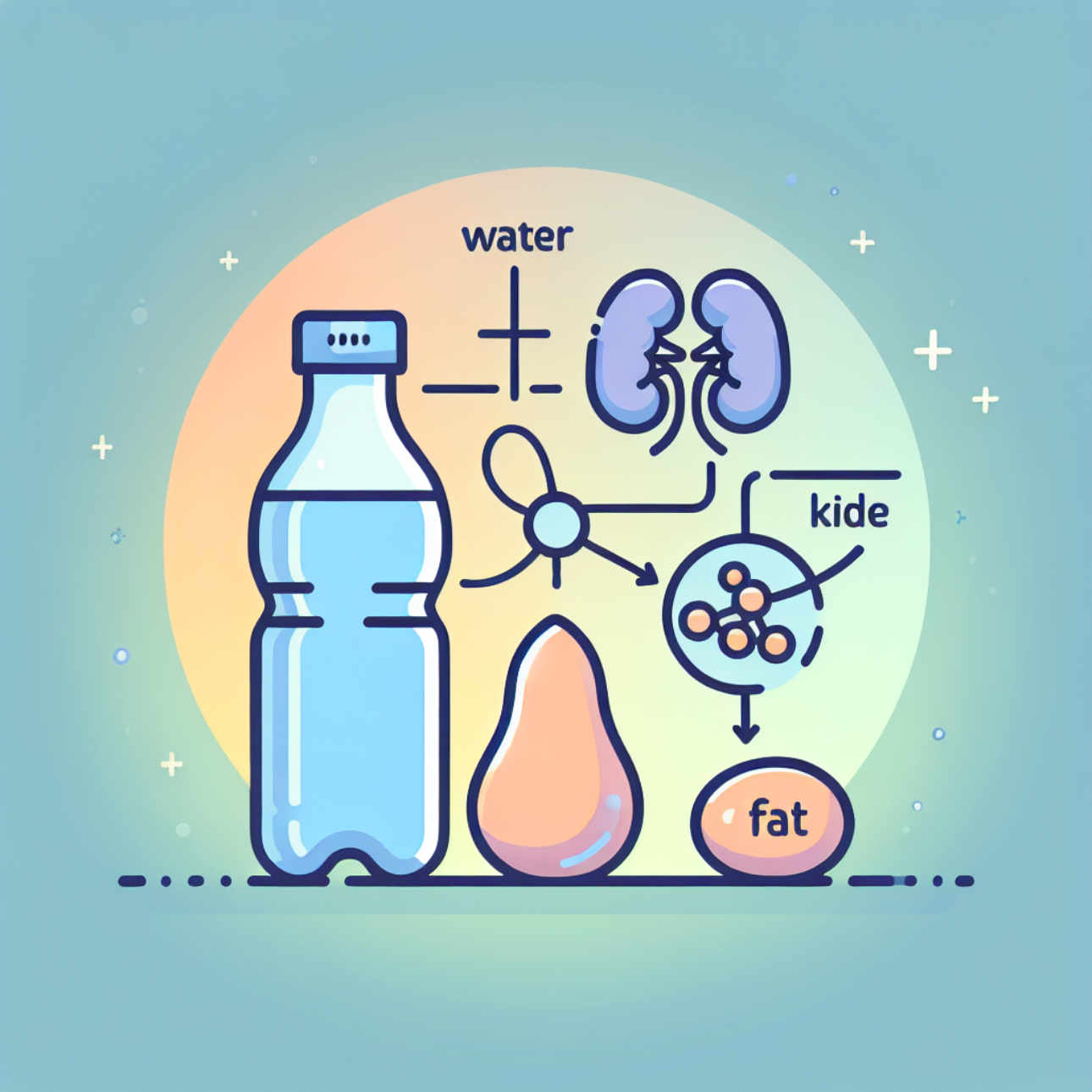
There are two main reasons why you might pee more often when entering ketosisA Deep Dive into the Metabolic State Transforming Health and Wellness Imagine your body as a hybrid car, capable of running on two distinct fuel sources: gasoline (carbohydrates) and electricity (fat). Ketosis is like switching your body’s engine from gasoline to electricity, primarily using fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates…. Read More (burning fatThe substance known as fat occupies a role far more complex and vital than often perceived. While frequently discussed in terms of diet and appearance, this tissue, properly termed adipose tissue when referring to the cellular mass, is a dynamic and essential component supporting a myriad of the body’s critical… Read More for fuel):
- Diuretic Effect: KetonesKetones, organic compounds produced by the liver, are the unsung heroes of energy metabolism, stepping in when glucose, the body’s primary fuel, becomes scarce. Think of them as a reserve power generator, kicking into gear when the main power supply (carbohydrates) is low. While often associated with the ketogenic diet,… Read More themselves are mild diuretics, meaning they cause your body to produce more urine. When your body starts producing ketones for energy, they enter your bloodstream. Your kidneys then work to filter these ketones out of your bloodBlood is the life force coursing through your veins and arteries, delivering vital oxygen and nutrients to every cell in your body while whisking away waste products. It’s a complex, dynamic fluid—not just a simple red liquid. Consider it a bustling highway system within your body, carrying various cellular vehicles… Read More and eliminate them through urine. This process increases urine production to get rid of the excess ketones.
- GlycogenGlycogen, a complex carbohydrate often dubbed “animal starch,” is the body’s primary storage form of glucose (sugar). Think of it as a strategic energy reserve, a reservoir of fuel readily available to power your muscles and brain when needed. While glucose circulates in your bloodstream, providing immediate energy, glycogen is… Read More Depletion: When you switch to ketosis, your body starts using stored glycogen (sugarSugar is a substance represented as a simple carbohydrate (a basic type of molecule made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) that serves as a vital component throughout the body. It is the primary source of energy for most cells, acting like the body’s main fuel. Every part of the body,… Read More) for energy instead of carbohydratesCarbohydrates, often called carbs for short, are organic molecules that your body uses for energy. They’re one type of fuel the body can use for energy. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, hence the name “carbohydrate” (carbo = carbon, hydrate = water). They come in simple… Read More from your diet. Glycogen is stored in your muscles and liverThe liver is a large organ located in the upper right part of the belly, under the rib cage. Like the heart that pumps blood or the lungs that help with breathing, the liver plays a crucial role in keeping the body healthy and working properly. This important organ is… Read More, and each gram of glycogen holds onto 3-4 grams of water. As your body depletes glycogen stores for energy, the water bound to that glycogen is released into your bloodstream, leading to increased urination.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Reduced Carbohydrate Intake: In ketosis, you consume fewer carbohydrates, causing your body to rely less on glucoseGlucose, a simple sugar (a sweet substance the body uses for energy), serves as a vital component in the human body, acting as the primary fuel for cells (tiny units that make up the body). Imagine the body as a bustling factory, where glucose is like the electricity powering the… Read More (blood sugarBlood sugar, also known as blood glucose, is a type of simple sugar circulating in your bloodstream. It can be a primary source of energy for your cells. Your body can get blood sugar from carbohydrates that you eat. The Word “Blood Sugar” This term is a modern invention, emerging… Read More) for energy.
- Glycogen Depletion: With less glucose available, your body taps into glycogen stores.
- Water Release: As glycogen breaks down, the water attached to it is released into your bloodstream.
- Increased Urine Production: Your kidneys filter out excess ketones and the released water, leading to more frequent urination.
Important Points:
- Frequent urination is a normal and expected side effect, especially when you’re new to ketosis.
- However, excessive thirst or dehydration can be a concern.
Here are some tips to stay hydrated while in ketosis:
- Drink plenty of water: Aim to drink throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
- Electrolyte Replenishment: Consider electrolyte supplements or drinks, especially if you experience fatigue or muscle cramps. ElectrolytesImagine your body as a vast network of interconnected wires, each carrying electrical impulses essential for life. Electrolytes are the tiny charged particles that create this vital current. They’re not some futuristic technology; they’re minerals dissolved in your body fluids, like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. These tiny powerhouses help… Read More like sodiumSodium is a soft, silvery-white metal that you might not think of when it comes to your health. But don’t let its straightforward appearance mislead you! Sodium is a crucial mineral that acts like a tiny conductor in your body, helping maintain a delicate balance for many functions, including metabolism…. Read More, potassiumPotassium, an often underestimated mineral, is a fundamental electrolyte crucial for a myriad of bodily functions. Think of it as the unsung conductor of the body’s orchestra, orchestrating the harmonious rhythm of nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and fluid balance. While its presence is ubiquitous in various foods, understanding potassium’s role… Read More, and magnesiumMagnesium is a superhero among minerals! It’s a shiny, silvery metal found abundantly in nature, but in your body, it acts more like a tiny maestro, conducting hundreds of essential metabolic reactions. • Synonyms: Well-documented synonyms for magnesium include: • Mg (chemical symbol) Etymology (Word Origins) • “Magnesium” comes from “Magnesia,”… Read More are lost through urination and need to be replenished.
- Monitor your urine color: Pale yellow urine indicates good hydration. Darker yellow urine suggests you might need to drink more fluids.t doesn’t improve with rest
- Confusion
Remember, everyone’s body reacts differently to ketosis. It’s important to listen to your body and stay hydrated. If you have any concerns, consult a healthcare professional or registered dietician for personalized advice.